The dedicated legal team of Caputo & Mariotti
Navigating Workers’ Compensation for Occupational Diseases
April 26, 2024
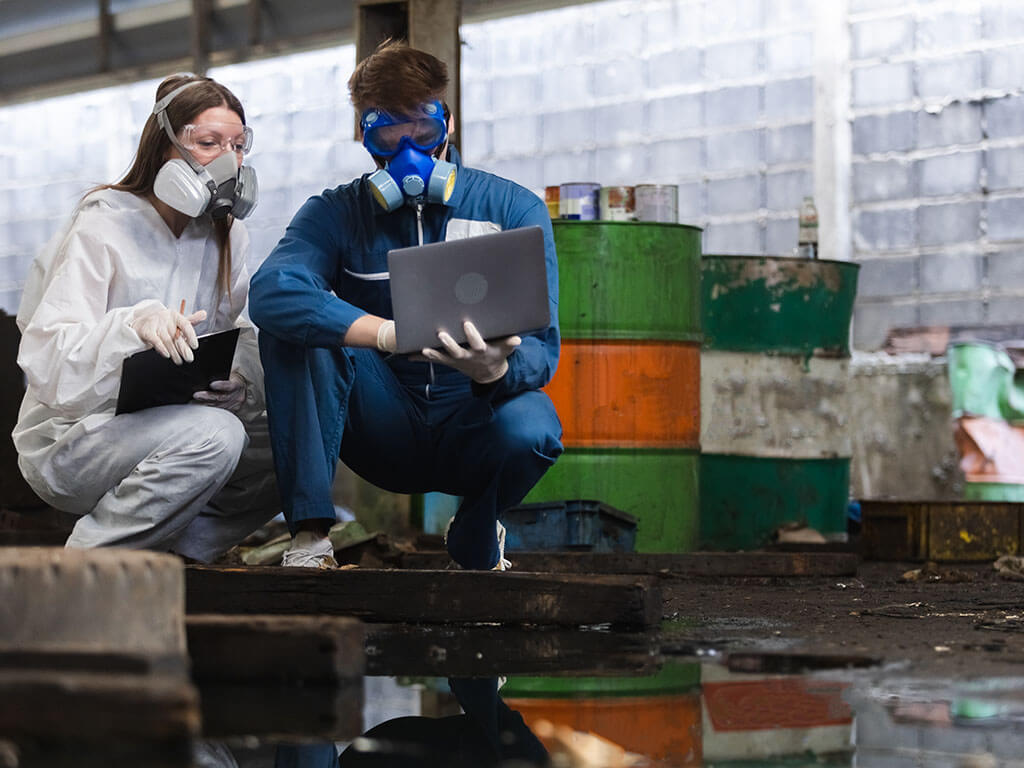
Introduction to Occupational Diseases
Occupational diseases are health conditions that develop over time due to exposure to harmful substances or environments at work. Unlike sudden injuries, these diseases often require proving a direct link to the workplace. Understanding this connection is crucial, as it determines your eligibility for workers’ compensation claims. Common occupational diseases include respiratory issues, skin disorders, and musculoskeletal injuries. It’s essential to recognize symptoms early and seek legal advice to ensure your rights are protected.
Proving Work-Relatedness
Proving that an occupational disease is work-related can be complex, requiring substantial medical evidence and sometimes expert testimony. This process is often challenging because symptoms may take years to manifest. Legal assistance can be invaluable in gathering documentation and presenting a compelling case. Our team at Caputo & Mariotti is experienced in handling such cases, ensuring that you receive the benefits you deserve. If you face similar challenges, don’t hesitate to schedule your free consultation.
Filing a Claim
Filing a claim for an occupational disease involves several steps, starting with notifying your employer and seeking medical attention. It’s crucial to document all interactions and medical visits meticulously. Our guide on handling work injuries provides a comprehensive overview of the process. In the event of a denial, understanding your rights and the appeals process is vital. Our firm can assist in navigating these procedures, ensuring that your case is presented effectively and your rights are upheld.
Handling Denials and Appeals
Despite efforts to provide comprehensive coverage, Workers’ Compensation claims for occupational diseases are sometimes denied by insurance carriers or employers. Common reasons for denial may include insufficient evidence of work-relatedness, disputes over the severity of the condition, or missed deadlines for filing the claim. In such cases, injured workers have the right to appeal the decision and seek a reconsideration of their claim.
Navigating denials and appeals can be complex, requiring a thorough understanding of state-specific Workers’ Compensation laws and procedures. Injured workers may need to gather additional evidence, obtain second opinions from medical experts, or present their case before an administrative law judge. Legal representation can be invaluable during this process, providing guidance on the best strategies for challenging denials and advocating for the worker’s rights.
Take the Next Step to Protect Your Rights
Occupational diseases can quietly disrupt your health, career, and financial stability but you don’t have to face these challenges alone. If your illness was caused by workplace exposure, you may be entitled to Workers’ Compensation benefits, even if your claim has been delayed or denied. The process can be complex, but having the right legal guidance can make all the difference.
At Caputo & Mariotti, we are committed to standing up for workers harmed by unsafe working conditions. Our experienced legal team understands how to prove work-related occupational diseases, challenge unfair denials, and fight for the full benefits you deserve. We take the burden off your shoulders so you can focus on your health and recovery.
If you believe your condition is related to your job or if you are struggling with a denied claim, do not wait. Contact Caputo & Mariotti today to schedule a free, confidential consultation. Let us review your case, explain your options, and advocate for your rights every step of the way. Your health, your livelihood, and your future are worth protecting.
FAQs
Q1: What is an occupational disease?
A: An occupational disease is a health condition caused by exposure to factors in the workplace. These diseases often develop gradually over time.
Q2: How can I prove my disease is work-related?
A: Proving work-relatedness requires medical documentation and sometimes expert testimony to establish a connection between your disease and your workplace.
Q3: What should I do if my claim is denied?
A: If your claim is denied, it’s important to understand the appeals process. Seeking legal advice can help you navigate these procedures effectively.
Q4: Are mental health issues covered by workers’ compensation?
A: Yes, mental health issues that are caused or aggravated by work-related factors can be covered under workers’ compensation, depending on state laws.

